[ad_1]
Rice University announces new process to revive lithium-battery anodes for reuse
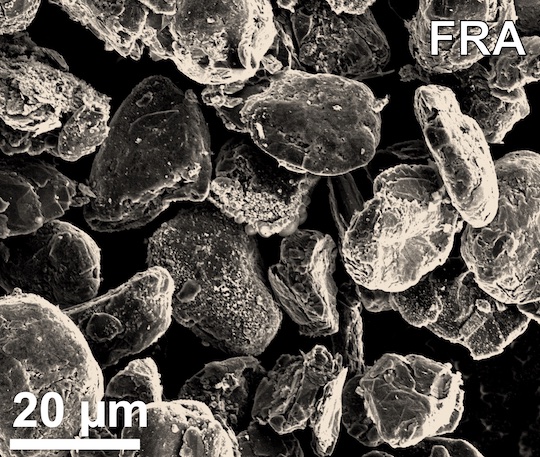

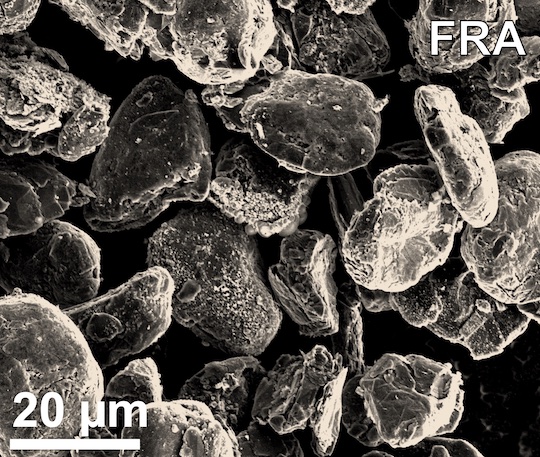
Rice University scientists have reported what they believe to be a partial solution to the mounting disposal problem of worn-out lithium-ion batteries. It relies on a unique “flash” Joule heating process they have developed to produce graphene from waste.
The lab of Rice chemist James Tour is said to have reconfigured the process to quickly regenerate graphite anode materials found in Li-ion batteries, removing impurities so they can be repeatedly reused. Powdered anodes from commercial batteries are “flashed” for a few seconds with a jolt of high energy, decomposing their inorganic salts, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which can then be recovered by processing them with dilute hydrochloric acid. The reported cost is about $118 to recycle one ton of untreated anode waste.
“We’re claiming our process can recover critical metals and recondition anodes in a far more environmentally and economically friendly manner,” says Tour.
Source: Rice University
[ad_2]
Source link